Perform Mouse Hover
Mouse hover actions in Selenium involve moving the mouse pointer over a web element without clicking it. This action is commonly used to reveal hidden elements, like dropdown menus, tooltips, or other interactive elements that appear only on mouseover.
How to Perform Mouse Hover Actions in Selenium:
To perform a mouse hover action, you typically use the Actions class in Selenium WebDriver, which provides advanced user interactions like hovering, clicking, dragging, and dropping.
- Basic
Initialize the WebDriver and Open the Page:
Set up the WebDriver and navigate to the desired web page.Locate the Web Element:
Identify the web element over which you want to hover the mouse.Use the Actions Class:
Create an instance of the Actions class and use it to perform the hover action.Perform the Action:
Use the move To Element() method to move the mouse to the specified element, and then call build() .perform() to execute the action.
package asc;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.interactions.Actions;
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
public class MouseHover {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://www.ebay.com/");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
WebElement element = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"vl-flyout-nav\"]/ul/li[9]/a"));
System.out.println(element);
Actions action = new Actions(driver);
action.moveToElement(element).perform();
}
}
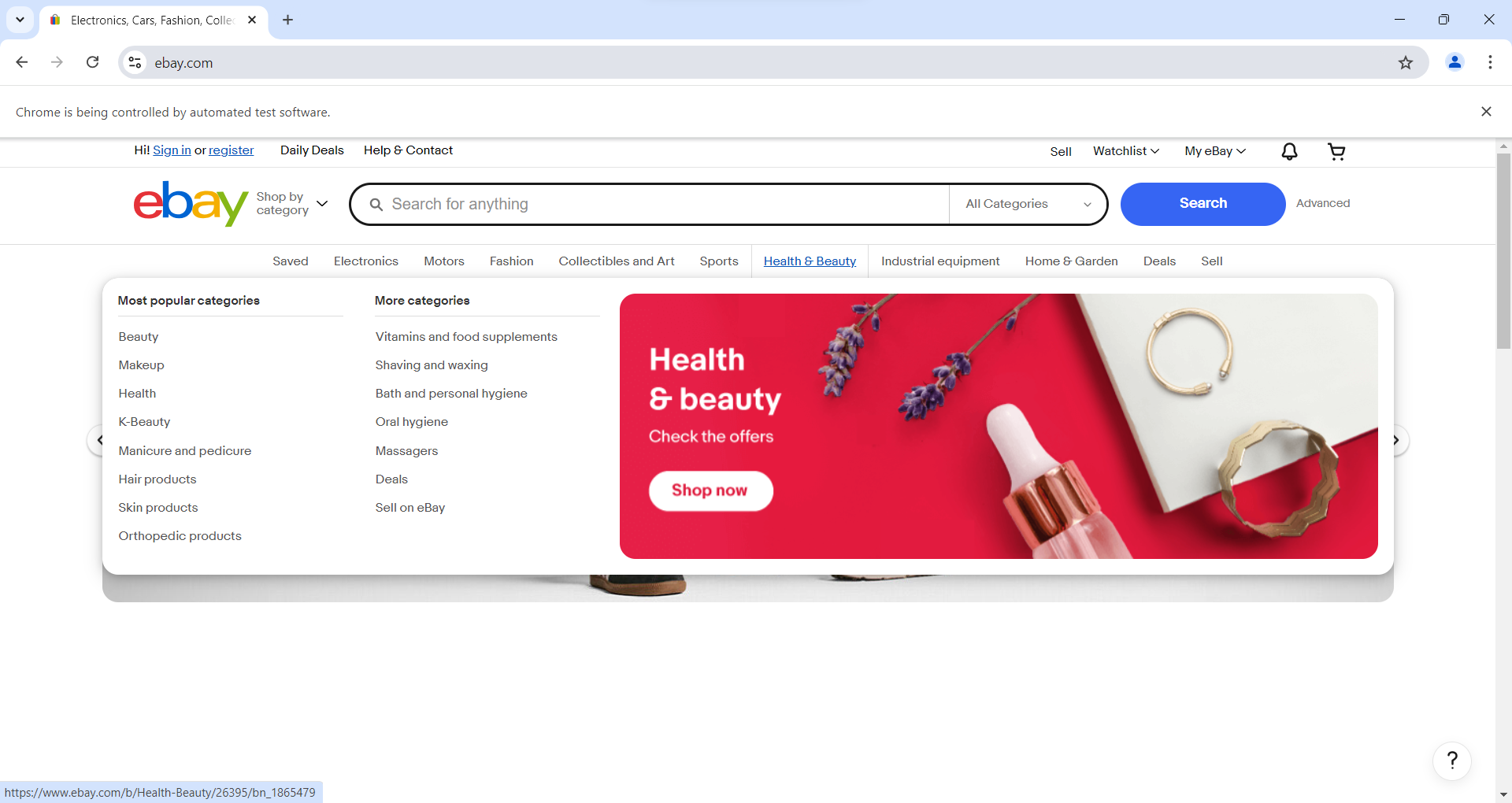
Output
Code Breakdown and Explanation:
1. Setup and Initialization:
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
ChromeDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();:
This sets up the ChromeDriver using WebDriverManager, ensuring the correct version of the ChromeDriver is used.new ChromeDriver();:
Initializes a new instance of the ChromeDriver, which is the WebDriver implementation for Google Chrome.
Opening the Website:
driver.get("https://www.ebay.com/");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.get("https://www.ebay.com/");:Navigates the browser to the eBay homepage.driver.manage().window().maximize();:
Maximizes the browser window for better visibility and interaction.
Locating the Web Element:
WebElement element = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"vl-flyout-nav\"]/ul/li[9]/a"));
river.findElement(By.xpath(...));:
Finds the specific web element on the page using an XPath expression. This XPath points to an anchor tag within a list item in a menu. In the context of eBay's website, this might correspond to a category in their navigation menu, such as "Motors," "Fashion," etc.
Printing the WebElement (Optional):
System.out.println(element);
System.out.println(element);:
Prints the WebElement to the console. This output typically includes a string representation of the element's details, useful for debugging.
Performing the Mouse Hover Action:
Actions action = new Actions(driver);
action.moveToElement(element).perform();
new Actions(driver);:
Creates an instance of the Actions class, which is used to perform advanced user interactions like mouse movements, clicks, drag-and-drop, etc.action.moveToElement(element).perform();:
Moves the mouse to the center of the specified element (element) and performs the hover action. This action usually triggers a change in the UI, such as displaying a dropdown menu or revealing additional options.
Key Points
WebDriverManager :
Actions Class :
XPath Locator:
Maximizing the Browser Window:
Considerations:
Element Identification:
Browser Compatibility:
Waits and Synchronization:
Mouse hover actions are particularly useful for interacting with dynamic content that appears only on mouseover, such as dropdown menus, tooltips, or interactive elements in navigation bars.
.png)